The reason why the lake remained liquid despite the increasing kinetic energy of methane molecules is due to the attraction between molecules. This force pulls them towards each other, making it difficult for them to break apart and transition into a gas state. It wasn’t until 2007 when enough energy was transferred to the lake to overcome this attraction, causing the methane to escape and the lake to freeze over.
What phase change did the methane lake change to?
For a minimum of five years, the lake received energy from the sun, which led to a rise in temperature. As a result, the molecules in the lake had more freedom of movement, causing the liquid methane to undergo a phase change and evaporate into a gas.
What temperature does methane evaporate?
According to previous studies, the typical rate of pure methane evaporation is (3.1 ± 0.6) × 10-4 kg s-1 m-2, with an average temperature of 94.1 ± 0.
6 K [6, 9].
What is liquid methane?
Triple-delimited paragraph:
“`While liquid methane is a cryogenic liquid, meaning it is extremely cold, it is also flammable. In fact, the temperature difference between the flame and the liquid methane right below it is over 3000°F!“`
What evidence card D says that more energy is transferred to the lake in summer than in any other season?
According to planetary geologists, the lake’s region has not experienced freezing temperatures for methane due to the summer season’s warmth. As per a scientist from the Universal Space Agency, the lake receives more energy during summer days because of the extended hours of sunlight. This energy transfer is higher than any other season, which explains why the lake remains unfrozen.
What cause liquid methane in the lake on titan to not evaporate between 2002 and 2007?
According to the students’ findings, the lake did not evaporate until 2007 despite it being summer since 2002. This is due to the attraction between molecules, which causes them to pull towards each other. Until 2007, there was not enough energy transferred to the lake to overcome this attraction, resulting in the delay of evaporation.
Why does an energy transfer not always result in phase change?
When ice is heated, the energy causes the bonds between the molecules to weaken and break, allowing the ice to transition into a liquid state. This process occurs without any change in the temperature of the molecules themselves, as the energy is solely focused on breaking the bonds. Essentially, the heat is used to overcome the forces holding the ice together, rather than increasing the temperature of the ice.
What never changes during a phase change?
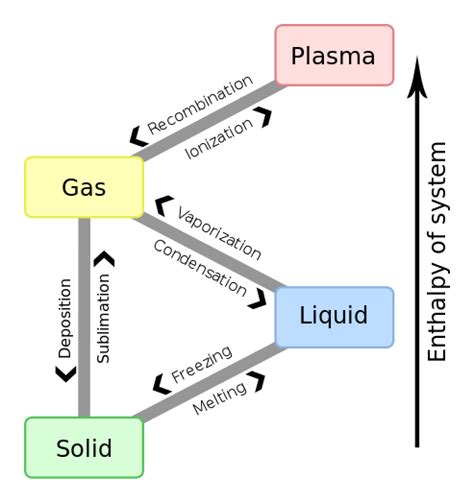
When a substance undergoes a phase change, such as from a solid to a liquid or a liquid to a gas, its temperature remains constant. This is because phase changes are isothermal, meaning that the temperature does not change during the process. For example, when ice melts into water, the temperature of the ice remains at 0 degrees Celsius until all of the ice has melted. This is due to the energy required to break the bonds between the molecules in the solid phase, which is absorbed as heat and keeps the temperature constant.
Similarly, when water boils and turns into steam, the temperature of the water remains at 100 degrees Celsius until all of the water has boiled away. Understanding the isothermal nature of phase changes is important in many fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
What determines whether or not a phase change occurs?
The occurrence of a phase change is dependent on the interplay between the kinetic energy of the molecules and the force of attraction that binds them together. It’s worth noting that the molecular attraction of a substance remains constant regardless of the phase it’s in.
What factors affect phase changes?
Changes in pressure, temperature, and chemical composition can trigger responses in various systems, leading to the creation, elimination, or alteration of phases. For instance, a low-density liquid can transform into a denser solid when subjected to increased pressure, while a solid can melt when exposed to higher temperatures. These transformations are essential in understanding the behavior of matter and its properties, and they have significant implications in various fields, including materials science, chemistry, and physics.
What are the 2 main factors that cause matter to change phase?
Phase changes occur due to changes in temperature or pressure within a system. As the temperature or pressure increases, the interaction between molecules intensifies, leading to a change in phase. Conversely, when the temperature decreases, molecules and atoms are more likely to settle into a more rigid structure, resulting in a phase change. These changes are a result of the delicate balance between the energy of the system and the forces holding the molecules together.
Understanding the factors that contribute to phase changes is crucial in fields such as materials science, chemistry, and physics.
What is it called when a liquid turns into a gas?
Boiling and evaporation are two processes that involve the transformation of a liquid into a gas. Evaporation occurs when a liquid turns into a gas at a temperature below its boiling point. This process happens at the surface of the liquid and is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure. Boiling, on the other hand, occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, and the vaporization process happens throughout the liquid.
This process is more rapid than evaporation and requires a higher amount of energy. Both processes are essential in our daily lives, from cooking to the water cycle, and understanding them can help us appreciate the science behind them.
What is it called when liquid turns to solid?
When a liquid is cooled, it undergoes a transformation and becomes a solid, a process known as freezing. As the temperature drops, the particles in the liquid slow down and eventually come to a stop, settling into a stable arrangement that forms a solid. Interestingly, the temperature at which freezing occurs is the same as the temperature at which melting occurs.
What is the 4th state of matter?
The 4th state of matter is plasma. Plasma is a highly ionized gas that contains free electrons and positive ions. It is created when a gas is heated to extremely high temperatures or exposed to a strong electromagnetic field. Plasma is found in lightning, stars, and neon signs.
It is also used in various industrial applications, such as welding, cutting, and sterilization. Plasma is important in the study of astrophysics and fusion energy research. Understanding the properties of plasma is crucial for developing new technologies and advancing our knowledge of the universe.
What eventually happens if energy is continually removed from a liquid?
“`When a liquid loses energy, it undergoes a phase change and becomes a solid. This phenomenon can be understood by considering the kinetic energy of the particles or molecules in the liquid and the intermolecular forces of attraction between them. As the energy decreases, the particles slow down and the attractive forces between them become stronger, causing them to arrange themselves in a more ordered structure, resulting in a solid state.“`
At what temperature does a liquid become a solid?
“`Water is typically found in a liquid state under normal atmospheric conditions. However, if the temperature drops below 0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit, water undergoes a phase change and becomes a solid substance known as ice.“`
Which phenomenon explains the drop in water level of a lake during the summer season?
During the fall season, lakes experience a phenomenon known as “autumn turnover.” This occurs when a significant portion of the lake’s volume loses oxygen during the summer months, leading to a rapid mixing of the water layers. This turnover is essential for the health of the lake’s ecosystem, as it helps to distribute nutrients and oxygen throughout the water column. However, it can also lead to the release of harmful gases, such as methane and hydrogen sulfide, which can be dangerous for aquatic life and humans alike.
It is important for scientists and policymakers to monitor and manage these turnovers to ensure the continued health and safety of our freshwater resources.
What happens when heat energy is added to a lake?
When heat is added to a lake, it typically gets mixed down mechanically due to the wind’s movement. This helps to maintain a relatively consistent temperature in the upper part of the lake.
Does a lake have more thermal energy?
The concept of temperature and thermal energy can be a bit confusing. Temperature is simply an average measurement, while thermal energy is the total amount of energy present. For example, a glass of water and Lake Superior may have the same temperature, but the lake has a much higher thermal energy due to the larger number of water molecules it contains. When it comes to measuring heat, the most commonly used units are the calorie and the joule (jool).
Would lakes be more or less likely to freeze in the winter if water had a lower specific heat?
If the specific heat capacity of water were lower, it would increase the likelihood of ponds and lakes freezing during the winter season. The specific heat of a substance refers to the energy required to be removed from the substance per unit mass to bring it closer to its freezing point.
Related Article
- Why Didn’T Drew Fuller Play In The Ultimate Life?
- Why Did The Villages Of Sumer Depend On Each Other?
- Why Did The Texas Senate Impose A Five-Ninths Rule?
- Why Did The Prisoner Choose The Bread Over The Key?
- Why Did The Lion Eat The Tightrope Walker Answer Key?
- Why Did The Chicken Cross The Basketball Court Worksheet Answers?
- Why Did The 30-60-90 Triangle Marry The 45-45-90 Triangle?
- Why Did Sonny Shoot The Guy In A Bronx Tale?
- Why Did Shang Kings Have Questions Scratched On Oracle Bones?
- Why Did My Ex Unfollow Me On Instagram Months Later?