There are several factors that have been linked to an increased risk of high-grade bleeding in leukemia patients. These include severe thrombocytopenia, which is a low platelet count, as well as reduced platelet function and abnormal coagulation parameters. Additionally, hyperleukocytosis, older age, and being female have also been identified as potential risk factors. It’s worth noting that these factors have been observed in mixed disease cohorts, meaning that they may not apply to all leukemia patients equally.
Why do vascular occlusion and infarct occur frequently with sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell disease causes red blood cells to lose their flexibility and become rigid, making it difficult for them to move through small blood vessels and capillaries. This can result in blockages that cause pain, tissue damage, and reduced blood flow to organs. Scientific research has shown that sickled RBCs have significantly reduced deformability, which contributes to the development of microvascular occlusion and related complications [3,7].
Why does leukemia cause anemia?
Leukemia is a complex disease with various types, and one of the most common symptoms is the rapid production of abnormal white blood cells. Unfortunately, these cells are not effective in fighting infections and can hinder the bone marrow’s ability to produce healthy cells, including red blood cells. As a result, anemia may occur, which can lead to fatigue, weakness, and other health complications.
What deficiency do patients with leukemia tend to have?
Studies have shown that leukemia cells have a greater need for iron to maintain their rapid growth compared to normal cells. This makes them more vulnerable to iron depletion, which can be targeted through treatment. By focusing on iron metabolism, leukemia cells can be induced to differentiate without causing harm to normal cells. This research highlights the potential for targeted therapies in the treatment of leukemia.
What type of anemia is associated with leukemia?
While aplastic anemia is not classified as a form of cancer, it may be linked to leukemia in some cases. Additionally, it can occur as a side effect of cancer treatments like intense chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which have the potential to harm healthy stem cells.
Is anemia associated with acute leukemia?
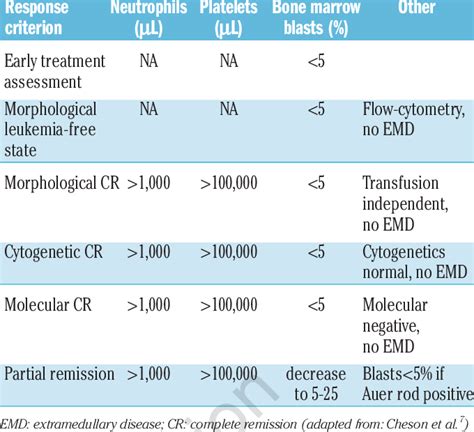
AML, or acute myeloid leukemia, is a prevalent form of leukemia that primarily affects adults. It is estimated that around 20,000 new cases of AML are diagnosed each year. The condition is characterized by the rapid multiplication of blasts, which can hinder the production of red blood cells and platelets. This can lead to anemia, causing fatigue, and increase the risk of bleeding due to a low platelet count.
Can leukemia cause severe anemia?
Yes, it is true that leukemia treatment can often result in anemia. According to Dr. experts, the majority of leukemia treatments can lead to a reduction in the production of other types of blood cells, such as platelets and red blood cells. This decrease in red blood cells can cause anemia, which is a condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to the body’s tissues.
It is important for patients undergoing leukemia treatment to be aware of this potential side effect and to work closely with their healthcare team to manage any symptoms of anemia that may arise.
Why is anemia a common complication of most cancers?
It’s not uncommon for cancer patients to experience anemia, which is characterized by a decrease in red blood cell production due to inflammation caused by the cancer itself. Furthermore, certain chemotherapies can be myelosuppressive, meaning they slow down the production of new blood cells in the bone marrow. Anemia can also be caused by kidney disease in some cases.
How does leukemia affect red blood cells?
Acute leukemia is a type of cancer that progresses rapidly, with immature malignant cells replacing healthy cells in the blood and bone marrow. As the cancerous cells continue to grow, they eventually stop producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, leading to anemia and an increased risk of infections for the patient.
What are the 3 crucial leukemia symptoms?
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It can be difficult to detect in its early stages, but there are some common signs and symptoms to look out for. These include fever or chills, persistent fatigue and weakness, and frequent or severe infections. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with your doctor as soon as possible.
Early detection and treatment can greatly improve your chances of recovery.
What is the deadliest leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a highly lethal form of leukemia. Unfortunately, the five-year survival rate for AML is only 29.5%. This type of cancer typically originates in white blood cells, but it can also begin in other types of blood cells.
What is the most aggressive form of leukemia?
Acute myelogenous leukemia, also known as AML, is a prevalent form of aggressive leukemia that primarily affects adults but can also impact children. This type of leukemia originates in the bone marrow’s myeloid cells and can rapidly spread throughout the bloodstream.
What is the hardest leukemia to treat?
Chronic leukemia is a type of blood cancer that progresses at a slower rate compared to acute leukemia. This type of cancer results in the accumulation of abnormal white blood cells that are relatively mature. Although it takes longer for chronic leukemia to cause noticeable problems, it can be more challenging to treat due to its slow growth. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of leukemia, such as fatigue, fever, or unexplained weight loss.
What is the best hospital in the US for leukemia?
The MD Anderson Leukemia Center is a globally renowned treatment facility for blood disorders and leukemia. The doctors at MD Anderson have conducted extensive research that has led to the development of new and improved standards of care for all forms of leukemia. Their groundbreaking work has helped countless patients receive the best possible treatment and care for their condition.
What type of leukemia is not curable?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that progresses slowly over time. In some cases, treatment may not be necessary, or only minimal treatment may be required. While there is currently no known cure for CLL, it is possible to manage the disease and keep it under control for many years. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your individual situation.
What is the slowest progressing leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a form of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. The bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are produced. CLL is referred to as “chronic” because it tends to progress at a slower rate than other types of leukemia. This means that individuals with CLL may not experience symptoms for many years, and the disease may not require immediate treatment.
However, it is important to monitor the condition closely and work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Is leukemia hemolytic anemia?
Studies have shown that individuals with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are more likely to experience autoimmune complications, with the most prevalent being autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), which occurs in approximately 7-10% of cases.
What does leukemia look like on a CBC?
When it comes to diagnosing leukemia, a complete blood count (CBC) is typically the go-to test. This diagnostic tool can detect abnormal levels of white blood cells, as well as low levels of red blood cells or platelets, which are all indicators of leukemia. If a patient’s CBC results show any of these abnormalities, further testing and treatment may be necessary.
What does leukemia look like on a blood test?
If you’ve recently undergone a blood count test and have been diagnosed with leukemia, it’s important to understand the results. Typically, individuals with leukemia will have higher levels of white blood cells, including leukemic cells, than what is considered normal. Additionally, it’s common to have lower than average counts of red blood cells and platelet cells. In some cases, all three types of blood cells may be low, which is referred to as pancytopenia.
It’s crucial to discuss your test results with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation.
What are signs of leukemia in blood work?
If you’re concerned about leukemia, your doctor may perform a complete blood count (CBC) to diagnose the condition. This test can detect the presence of leukemic cells in your blood. Additionally, abnormal levels of white blood cells, red blood cells, or platelets may also indicate leukemia.
Related Article
- Why Is Cold Air Coming Out Of My Electrical Outlet?
- Why Is Christmas The Most Wonderful Time Of The Year?
- Why Is Cash App Saying My Zip Code Is Invalid?
- Why Is Cash App Saying My Request Cannot Be Sent?
- Why Is Biomass A Better Alternative To Natural Gas Apex?
- Why Is An I Beam Stronger Than A Rectangular Beam?
- Why Is Air Backfeeding From My Trailer Emergency Supply Line?
- Why Is A Raisin In The Sun Still Relevant Today?
- Why Is A Graduated Cylinder More Precise Than A Beaker?
- Why Is A Crystal Of Strontium Chloride An Extended Structure?